Understanding Three-Way Matching – The Foundation of Purchase Order Control
Part 1: What Three-Way Matching Actually Is
The Fundamental Problem:
Here’s what happens in many businesses: Finance receives an invoice. Someone has to figure out:
- Did we actually order this?
- Did we receive it?
- Do the numbers match?
This detective work happens for every invoice. It’s time-consuming. Things slip through. Suppliers sometimes invoice for items not delivered. Quantities don’t match. Prices differ from what was agreed.
The Three Documents:
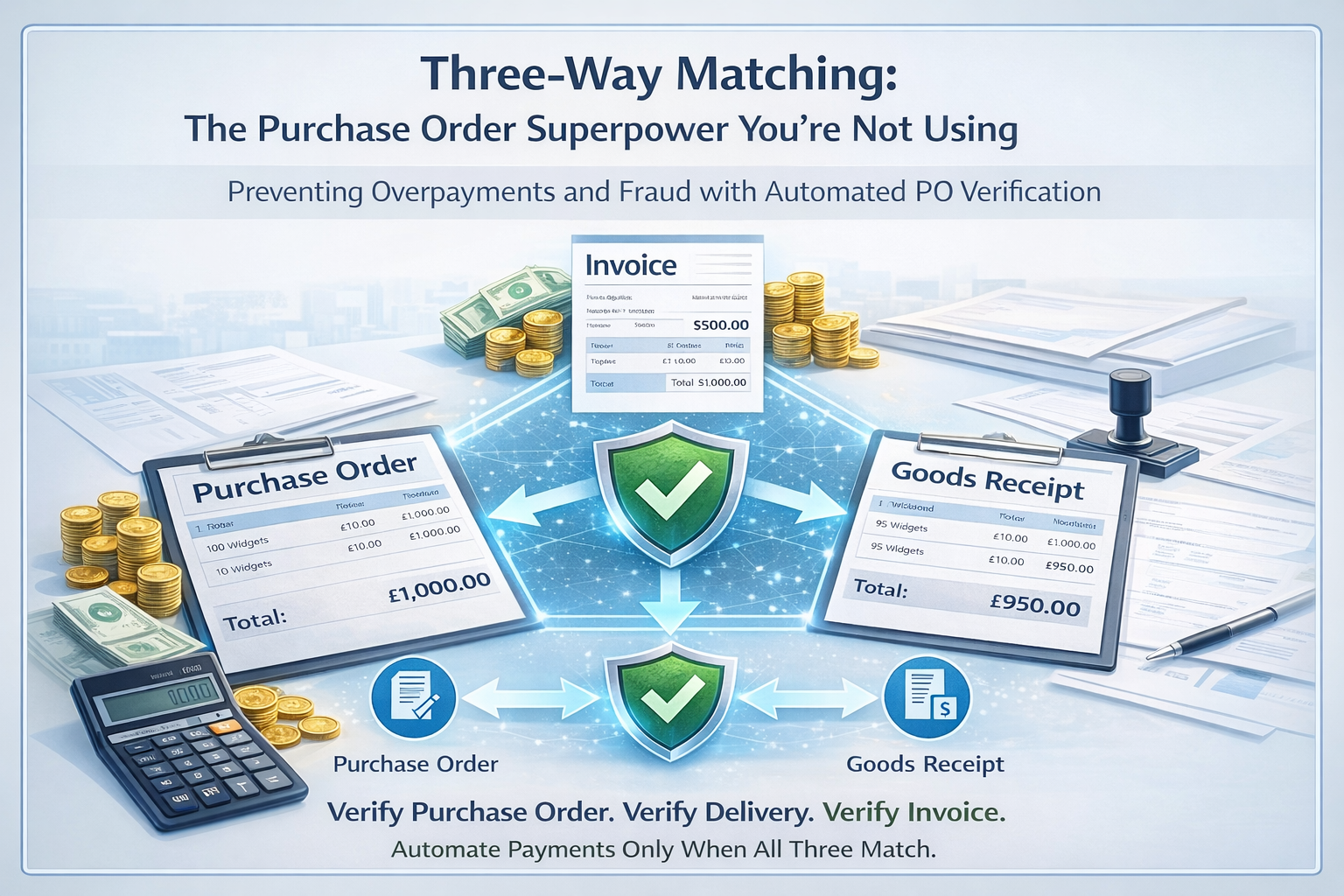
Three-way matching compares three documents against each other:
- Purchase Order: What you agreed to buy
- Goods Receipt: What you actually received
- Invoice: What the supplier is billing you for
The concept is simple: these three should align. If they do, pay the invoice. If they don’t, investigate before paying.
Why This Matters More Than You Think:
Without matching:
- You might pay for goods not received
- Prices might differ from what was agreed
- Quantities might be wrong
- Duplicate invoices might get paid
- No systematic check exists
With matching:
- Only pay for what was actually received
- Ensure agreed prices
- Catch errors before payment
- Prevent duplicate payments
- Create an audit trail
Ready to let AI protect your procurement?
Contact Systematics Software Ltd today to explore how AI-powered solutions can revolutionise your operations and prepare you for the future of technology.
Nam aliquet ante porta, gravida elit, at fringilla felis suscipit.
How It Works in Practice:
Step 1: Purchase Order is Created
- Specific items, quantities, prices agreed
- Delivery date set
- Terms confirmed
- This becomes the “contract” reference
Step 2: Goods Arrive
- Receiving team logs what actually arrived
- Quantities received
- Condition noted
- Date recorded
- Linked to the PO
Step 3: Invoice Arrives
- Supplier sends invoice
- System finds the matching PO
- Finds the goods receipt
- Compares all three
Step 4: The Matching Logic
The system checks:
- Supplier match: Same supplier on all three documents?
- PO reference: Does invoice reference the right PO?
- Items match: Are invoiced items the ones that were ordered and received?
- Quantities align: Invoice quantity ≤ received quantity ≤ ordered quantity?
- Prices match: Invoice prices = PO prices?
- Calculations correct: Does the arithmetic add up?
Step 5: Outcomes
Perfect Match (Ideal): All three documents align perfectly within acceptable tolerances. Invoice approved automatically for payment. No human intervention needed.
Minor Discrepancy (Common): Small variance within defined parameters – perhaps a 2% price difference, or one extra unit delivered. Flagged for quick review. Usually approved within minutes.
Major Discrepancy (Requires Action): Significant mismatch. System blocks payment. Clear documentation of what doesn’t match. Routed to appropriate person to investigate.
Ready to deploy AI protection across your procurement?
Contact Systematics Software Ltd today to explore how AI-powered solutions can revolutionise your operations and prepare you for the future of technology.
Nam aliquet ante porta, gravida elit, at fringilla felis suscipit.
The Tolerance Question:
Perfect matches are rare because business is messy:
- Suppliers round prices
- Delivery quantities vary slightly for bulk items
- Exchange rates fluctuate for international purchases
- Discounts get applied at different stages
So you define tolerances:
- Price tolerance: ±2% acceptable?
- Quantity tolerance: +5%/-0% for perishables?
- Timing tolerance: Invoice within 90 days of delivery?
These tolerances let you auto-process good-enough matches while catching genuine problems.
Understanding Partial Deliveries:
Real business is rarely clean. You order 100 items:
- 60 arrive week one
- 30 arrive week two
- 10 are cancelled
The supplier might invoice:
- Once for each delivery
- Once for all 90 items
- At different times
Your matching system needs to handle this complexity. It tracks cumulative deliveries against the PO and ensures invoicing doesn’t exceed what was actually received.
The Data Quality Connection:
Three-way matching forces data discipline:
- POs must be accurate (they’re the reference point)
- Goods receipt must be logged properly
- Invoices must reference POs correctly
This discipline creates clean, reliable data. And clean data is what makes AI and analytics possible.
When every transaction has complete data – what was ordered, what was received, what was paid – you can:
- Analyse supplier reliability (do they deliver what they promise?)
- Identify cost trends (are prices creeping up?)
- Forecast accurately (based on real transaction patterns)
- Detect anomalies (unusual patterns that might indicate fraud or errors)
Want to discuss whether three-way matching makes sense for your business?
Every business is different, and what works for one might not work for another. I’m happy to share what I’ve learned about when it works well and when it doesn’t.
Book a time to talk: https://calendly.com/jiteshlakhani
Or call: 0207 031 9810